University of Tokyo clinical study: Long-term supplementation of NMN can enhance muscle strength in the older people
There was also an increased risk of Sarcopenia, which accelerates the loss of muscle mass and strength, leading to an increased risk of falls and even death in older adults.
Since skeletal muscle is the “energy hog” in the human body, and NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is closely related to the production process of cellular energy, some scholars have speculated that increasing NAD+ levels may help alleviate and treat sarcopenia.
In 2022, scholars at the University of Tokyo in Japan conducted a randomized double-blind clinical trial and found that oral NMN supplementation in older men could increase NAD+ levels and enhance their muscle strength. The study was published in the journal Nature Partner Journals Aging in May of the same year.
In the study, 20 older men evenly divided into the NMN group and the placebo group, with an average age of about 71 in both groups. Ten participants in the NMN group received 250mg of NMN orally every day for 12 weeks. Those in the placebo group given the same amount.
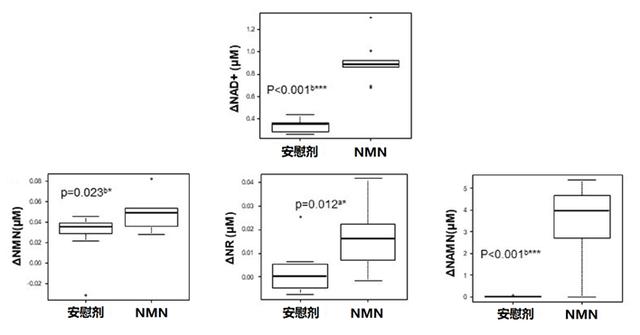
The results showed that 250mg/ day of oral NMN did not cause adverse reactions in the subjects, and there were no abnormalities in the basic indicators in their bodies. In addition, NMN supplementation also significantly increased the levels of NAD+ and related metabolites in the subjects, and the increase of NAD+ was particularly prominent.
In addition, the researchers also used clinical criteria for diagnosing sarcopenia to test the participants’ walking speed and grip strength.
The results showed that although NMN supplementation did not increase the muscle mass of the subjects, their walking speed and grip strength did improve. In other words, supplementing with NMN has the potential to help combat sarcopenia caused by aging.
summary, this clinical trial demonstrated the safety of oral NMN of 250mg/ day and significantly increased NAD+ levels in subjects.
In addition, NMN supplementation also helps to slow the decline in muscle function caused by aging. However, this study also has some shortcomings. For example, the subjects are only old men around 70 years old, and older people and female groups not involved. In addition, the sample size of the experiment is also small, so the conclusion of the paper needs further study.
References:
1. Igarashi, M., Nakagawa-Nagahama, Y., Miura, M. et al. Chronic nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation elevates blood nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide levels and alters muscle function in healthy older men. npj Aging 8, 5 (2022).

