Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a product of the nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase reaction and a key NAD + intermediate.
NMN has shown unique functions in promoting liver gluconeogenesis, insulin secretion, muscle insulin sensitivity, and adipogenesis in adipose tissue.
In particular, NMN also contributes to the maintenance of intestinal health, including the integrity of the intestinal epithelium, the structure of the intestinal microbiome, and the homeostasis of intestinal metabolism.
On this basis, the researchers explored the potential beneficial role of NMN in improving gut health.
01 NAD+ and intestinal function
A growing number of studies have linked changes in gut function to NAD+ deficiency. Some chronic intestinal diseases with altered immunomodulatory basis are associated with NAD+ deficiency, suggesting a bidirectional relationship between NAD+ depletion and intestinal inflammation.
Increasing NAD+ can alleviate intestinal inflammation, and studies suggest that NAD+ deficiency may promote intestinal inflammation and leakage, negatively affecting the gut microbiome and overall host physiology.
NAD + depletion can lead to a range of age-related problems, including neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, cardiovascular disease, and muscle atrophy.
In addition, NAD + can also stimulate intestinal goblet cells to secrete mucus and maintain the integrity of intestinal mucosa, which proves that NAD + can protect intestinal homeostasis to a certain extent.
NAD+ deficiency and intestinal inflammation
1 Inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease is a heterogeneous chronic digestive syndrome characterized by impaired intestinal barrier and abnormal intestinal repair, and in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, abnormal NAD+ metabolism and increased consumption of NAD by NAD-consuming enzymes (PARP and CD38) suggest a link between NAD metabolism and inflammatory bowel disease.
2 Autism spectrum disorder
Gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhea, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, and gastroesophageal reflux are common comorbidities of autism spectrum disorders, and increased intestinal permeability is associated with disruption of the tryptophane-NA metabolic pathway.
3 Metabolic disease
Metabolic diseases, such as obesity and diabetes, are often characterized by disorders of NAD+ metabolism. In fact, NAD+ reduction may lead to adverse metabolic complications associated with obesity and diabetes, and the abolition of NAMPT in intestinal epithelial cells can lead to lower local NAD+ levels and impair intestinal physiology.

02 NMN maintains intestinal health
NMN, a precursor to NAD+, has been shown to regulate gut microbiota and inflammation in different dietary and pharmacological mouse models with impaired gastrointestinal barrier function.
1 Experiment to increase levels of beneficial gut bacteria
Studies have shown that taking NMN can significantly increase serum NAD+ levels.
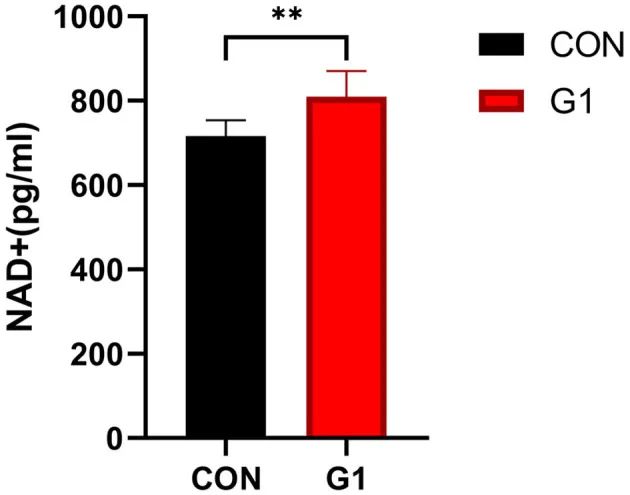
Long-term use of NMN increases levels of beneficial gut bacteria, such as Lactobacillus, bifidobacterium, Prevotella and Ackermannia.
The latter, a symbiotic gut bacterium linked to metabolic health as well as reduced risk of obesity and diabetes, is known to produce butyric acid and have probiotic properties.
There is also a significant decrease in the presence of harmful bacteria in the gut microbiota, such as Biliophilus, Fibrillator and desulvibrionaceae. This change in gut microbiota composition has linked to improved gut barrier function, reduced inflammation, and increased gut mucus secretion.
In addition, NMN supplementation may also improve the expression of genes involved in maintaining intestinal homeostasis and prevent disruption of intestinal barrier function caused by a high-fat diet.
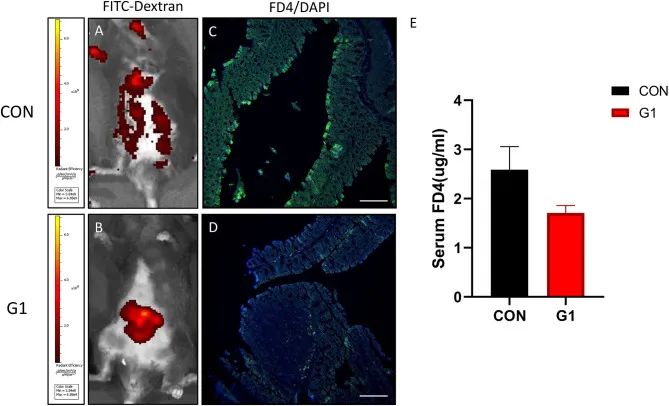
NMN has shown potential to improve the morphology and barrier function of the inflamed intestine.
In fact, NMN significantly increased the relative fecal abundance of Firmicutes, verrucobacteria, Ackermannia and Lactobacillus, which considered beneficial bacteria involved in the production of SCFA (acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid).
In addition, the number of unclassified Bacteroidetes and Muriaceae members decreased. Although NMN cannot completely relieve intestinal inflammation, supplementing it has the potential to prevent the development of the disease and reduce the pain caused by inflammatory bowel disease.

2 Experiment to reshape the gut microbiota
The study also found that NMN supplementation was effective in other conditions related to intestinal homeostasis disorders.
For example, in radiation-induced gastrointestinal injury, C57BL/6J mice receiving 15 Gy abdominal irradiation and NMN supplementation in drinking water (300 mg/kg/ day), long-term NMN supplementation mitigated intestinal fibrosis and reshaping the composition and function of the gut microbiota disrupted by ionizing radiation (IR).
In addition, Ackermannia and metabolism-related pathways were more abundant in the irradiated mice after treatment with NMN.
3 Experiment to improve intestinal dysfunction
NMN can also improve intestinal dysfunction and dysbiosis associated with other intestinal discomfort conditions, such as those caused by sleep deprivation in mice.
Studies have shown that NMN not only improves intestinal physiology and microbiota, but also restores colonization resistance to intestinal infections.
The gut microbiome is very important to the human body
Food decomposition, the synthesis of essential vitamins, etc., require the cooperation of the microbiome, and at the same time, the microbiome can maintain the integrity of the intestinal lining and regulate human immunity.
Supplementation of NMN conducive to improving the stability and adaptability of intestinal flora, and NMN can increase the level of NAD+, thereby increasing the antioxidant level, reducing inflammation, and increasing the function of intestinal barrier.
provide high quality β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) raw materials, products exported to Europe, America, Korea, India and other parts of the world, if you interested in our products, please feel free to contact us, will happy to provide you with any information you need.
The content of this article is provided as information only, does not represent the position and recommendations of the Department, and is not a substitute for medical diagnosis and recommendations.
reference
- [1] Niño-Narvión J, Rojo-López MI, Martinez-Santos P, Rossell J, Ruiz-Alcaraz AJ, Alonso N, Ramos-Molina B, Mauricio D, Julve J. NAD+ Precursors and Intestinal Inflammation: Therapeutic Insights Involving Gut Microbiota. Nutrients. 2023 Jun 30;15(13):2992. doi: 10.3390/nu15132992. PMID: 37447318; PMCID: PMC10346866.
- [2] Nagahisa T, Yamaguchi S, Kosugi S, Homma K, Miyashita K, Irie J, Yoshino J, Itoh H. Intestinal Epithelial NAD+ Biosynthesis Regulates GLP-1 Production and Postprandial Glucose Metabolism in Mice. Endocrinology. 2022 Apr 1;163(4):bqac023. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqac023. Erratum in: Endocrinology. 2022 Jun 1;163(6): PMID: 35218657.
- [3] Huang P, Jiang A, Wang X, Zhou Y, Tang W, Ren C, Qian X, Zhou Z, Gong A. NMN Maintains Intestinal Homeostasis by Regulating the Gut Microbiota. Front Nutr. 2021 Jul 29;8:714604. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.714604. PMID: 34395502; PMCID: PMC8358781.
- [4] Zhao X, Ji K, Zhang M, Huang H, Wang F, Liu Y, Liu Q. NMN alleviates radiation-induced intestinal fibrosis by modulating gut microbiota. Int J Radiat Biol. 2023;99(5):823-834. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2023.2145029. Epub 2022 Nov 16. PMID: 36343364.
