A recent study found that NMN mitigated the effects of age-related macular degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of vision loss in adults, affecting 20-30% of people over the age of 75 in developed countries.
People with AMD have difficulty reading, recognizing faces, and visualizing details. But current treatments for AMD only treat about 10 percent of patients with “wet” AMD, in which blood vessels grow into the center of the eye.
There are currently no treatment options for the other 90 percent of patients with “dry” AMD, who have lost cells in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue of the eye.
Past research has shown that defects in the mitochondria, the energy generators of cells, are a key aspect of AMD disease, and a new study suggests that targeting the organelles could treat dry AMD.
A team of researchers at the University of Minnesota Ophthalmology published a study in REDOX Biology in which they treated mitochondrial dysfunction in cells of AMD patients with four molecules: n-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), rapamycin, pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ), and niacinamide mononucleotide (NMN).
Cells from different AMD patients showed different responses to each drug, suggesting that it is possible to develop personalized treatments for AMD patients.
In other words, some treatments work well for some patients and not for others, so clinicians can assess which treatments work best for each individual.
Mitochondrial regulators improve energy production in retinal cells
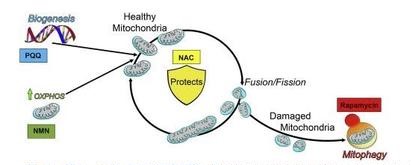
Ebeling and colleagues selected the four molecules based on their effects on mitochondria.
NAC increases the cellular amount of the energy molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by protecting mitochondria from oxidative stress, thereby increasing the amount of mitochondria that produce ATP.
PQQ can increase mitochondrial content in cells by stimulating the production of mitochondria. Rapamycin increases the number of mitochondria and induces the disposal of defective mitochondria from the cell, a process called mitochondrial autophagy.
NMN increases the concentration of a molecule called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), which promotes energy production and health in cells.
By measuring ATP levels, scientists can assess mitochondrial function. Ebeling and colleagues treated donor eye cells with these four molecules, which only improved mitochondrial function in some AMD patients.
Of the four molecules, rapamycin, PQQ, and NMN significantly increased ATP levels in patients’ retinal cells, while NAC did not.
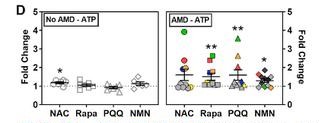
Depending on the patient, the cells show a highly personalized response to these four molecules.
The treatment improved mitochondrial function in half of the patients’ retinal cells by 50 to 350 percent,
while in the other half, mitochondrial function improved by 5 to 25 percent.
The University of Minnesota found that of the four molecules, PQQ was the most effective at improving mitochondrial function.
“These results support the idea that an individualized approach is needed to treat AMD.” Developing ways to pre-screen patients to determine the best type of intervention is key to finding effective treatments for AMD.”
Source
- 1. Ebeling MC, Polanco JR, Qu J, Tu C, Montezuma SR, Ferrington DA. Improving retinal mitochondrial function as a treatment for age-related macular degeneration [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 18]. Redox Biol. 2020;101552. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101552
Journal Reference
- 1. Friedman DS, O’Colmain BJ, Muñoz B, et al. Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in the United States [published correction appears in Arch Ophthalmol. 2011 Sep;129(9):1188]. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122(4):564-572. doi:10.1001/archopht.122.4.564
- 2. Wong WL, Su X, Li X, et al. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(2):e106-e116. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70145-1

